Malicious Listener for Ivanti Endpoint Mobile Management Systems
Malware Analysis at a Glance |
|
|---|---|
| Executive Summary | The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) obtained two sets of malware from an organization compromised by cyber threat actors exploiting CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428 in Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (Ivanti EPMM). Each set contains loaders for malicious listeners that enable cyber threat actors to run arbitrary code on the compromised server. |
| Affected Products | Ivanti EPMM, versions 11.12.0.4 and prior, 12.3.0.1 and prior, 12.4.0.1 and prior, and 12.5.0.0 and prior. (Ivanti provided a patch and disclosed the vulnerabilities on May 13, 2025.) |
| Key Actions |
|
| Indicators of Compromise | For a downloadable copy of IOCs associated with this malware, see: MAR-251126.r1.v1.CLEAR. |
| Detection |
This malware analysis report includes YARA and SIGMA rules. For a downloadable copy of the SIGMA rule associated with this malware, see: AR25-260A/B SIGMA YAML. |
| Intended Audience |
Organizations: All organizations with on-premises Ivanti EPMM systems. Roles: Digital forensics analysts, incident responders, vulnerability analysts, system administrators. |
Introduction
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) obtained two sets of malware, five files in total, from an organization where cyber threat actors exploited CVE-2025-4427 [CWE-288: Authentication Bypass Using an Alternate Path or Channel] and CVE-2025-4428 [CWE-‘Code Injection’] in Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (Ivanti EPMM) deployments for initial access.
Note: Ivanti provided a patch and disclosed the vulnerabilities on May 13, 2025. CISA added both vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog on May 19, 2025.
Around May 15, 2025, following publication of a proof of concept, the cyber threat actors gained access to the server running EPMM by chaining these vulnerabilities. The cyber threat actors targeted the /mifs/rs/api/v2/ endpoint with HTTP GET requests and used the ?format= parameter to send malicious remote commands. The commands enabled the threat actors to collect system information, download malicious files, list the root directory, map the network, execute scripts to create a heapdump, and dump Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) credentials.
CISA analyzed two sets of malicious files the cyber threat actors wrote to the /tmp directory. Each set of malware enabled persistence by allowing the cyber threat actors to inject and run arbitrary code on the compromised server.
CISA encourages organizations to use the indicators of compromise (IOCs) and detection signatures in this Malware Analysis Report to identify malware samples. If identified, follow the guidance in the Incident Response section of this Malware Analysis Report. Additionally, organizations should ensure they are running the latest version of Ivanti EPMM as soon as possible.
Download the PDF version of this report:
For a downloadable copy of IOCs associated with this malware, see:
For a downloadable copy of the SIGMA rule associated with this malware, see:
Malware Summary
CISA analyzed two sets of malware:
- Set 1 consists of the following malicious files:
web-install.jar,ReflectUtil.class, andSecurityHandlerWanListener.class. - Set 2 consists of the following malicious files:
web-install.jarandWebAndroidAppInstaller.class.
Note: To distinguish the set 1 malware, named web-install.jar, from the set 2 malware with the same name, hereafter this Malware Analysis Report will refer to:
- Set 1’s
web-install.jaras Loader 1. - Set 2’s
web-install.jaras Loader 2.
Each set contains a loader and malicious listener that enables cyber threat actors to inject and run arbitrary code on the compromised server.
Set 1 works together in the following ways:
- Loader 1 contains and loads
ReflectUtil.class.ReflectUtil.classinjects and managesSecurityHandlerWanListenerin Apache Tomcat.SecurityHandlerWanListener.classintercepts specific HTTP requests and processes them to decode and decrypt payloads, which create a new class that cyber threat actors can execute to run arbitrary code.
Set 2 works together in the following ways:
- Loader 2 contains and loads
WebAndroidAppInstaller.classat runtime.WebAndroidAppInstaller.classintercepts and processes specific HTTP requests, retrieves and decrypts password parameters from the request, defines and loads a new malicious class, encrypts and encodes the new class output, and generates a response with the encrypted output.
Malware Delivery
Note: This advisory uses the MITRE ATT&CK® for Enterprise framework, version 17. See Appendix A: MITRE ATT&CK Techniques for a table of the threat actors’ activity mapped to MITRE ATT&CK tactics and techniques.
The cyber threat actors delivered this malware in segments, splitting Loader 1 and 2 into multiple Base64-encoded segments [T1027.004]. They delivered each segment via separate HTTP GET requests and then used Java Expression Language (EL) injection to write each chunk and append them together using the append mode (via the true parameter).
For each loader, the actors’ first GET request created the file and wrote chunk 1. Their subsequent requests appended chunks to the existing file. Below is an example of the actors’ GET request.
"GET /mifs/rs/api/v2/featureusage?format=${"".getClass().forName("java.io.FileOutputStream").getConstructor("".getClass(), "".getClass().forName("[Z").getComponentType()).newInstance("/tmp/web-install.jar", true).write("".getClass().forName("java.util.Base64").getMethod("getDecoder").invoke(null).decode("[BASE64_CHUNK]"))
This argument creates/appends malware segments to the following file:
.newInstance("/tmp/web-install.jar", true).
It then writes the following decoded Base64 chunk:
.write("".getClass().forName("java.util.Base64").getMethod("getDecoder").invoke(null).decode("[BASE64_CHUNK]")).
This technique is used for defense evasion—it enables the malware to evade signature-based detection and size limitations as it is transferred to the system. Holistically, this technique combines chunked encoding for evasion and file append operations for reconstruction.
Malware Metadata
Set 1
See Table 1 through Table 3 for metadata of the analyzed malware.
| Filename | web-install.jar |
|---|---|
| Size | 30996 bytes |
| Type | JAR |
| MD5 | e33103767524879293d1b576a8b6257d |
| SHA1 | c2046523f1cb487a473b0a46a5a4a957f1b3200a |
| SHA256 | c1f60ca5a5f7b94ab7122718a44b46de16c69d22c2eb62ce2948cab14bc78d50 |
| SHA512 | 004b71ebeb4808b6dfdc4e58b95c4b307985c08118c45c02a34cd56ff697259199698989af0725d63802dfc785a72e416d2db5875edd1a0fa80ae01a282b2007 |
| ssdeep | 384:kaD+TLeDOl+mDcDFNUaD+TLeDOl+mDcDFNUaD+TLeDOl+mDcDFNUaD+TLeDOl+ms:z6Pl+mwj6Pl+mwj6Pl+mwj6Pl+mw3 |
| Entropy | 7.951890 |
| Filename | ReflectUtil.class |
|---|---|
| Size | 11886 bytes |
| Type | compiled Java class data, version 49.0 (Java 1.5) |
| MD5 | 6ec2169312feb9fde0b17e244b32c37d |
| SHA1 | 6d7e85862f925e83f6d0c29e291765548fac721a |
| SHA256 | 065c1c2fb17ba1c3f882bead409215df612673cd455698768ed71412f9190ba3 |
| SHA512 | 4cd26b298b448db6b26d91b8cf7ac169d693a0dad4f184742463db872b809b91d462ab4659bb21474578e3202bfc92b0db18716db6b4c3c24b3f9e7f2fccce27 |
| ssdeep | 192:KuZ4E9i44LYcyHCi3uFl0xEHqQ+k5bUW0sbh3aUfPuS6GZz:Ku79BP/3uFygq49V0stKEuSpz |
| Entropy | 6.258794 |
| Filename | SecurityHandlerWanListener.class |
|---|---|
| Size | 4690 bytes |
| Type | compiled Java class data, version 49.0 (Java 1.5) |
| MD5 | 5e9d283b483b8d5c637baf7cfdda0e08 |
| SHA1 | 8b87a881f6f81afb596d3f98abef4225315e26bf |
| SHA256 | b1b1cf33b8d3da35293d6b74c378f0cd9452a4351e26d07c896c4d9a8257ef89 |
| SHA512 | 07956b3a830bd0885202d9bc7a5b5a5927acf1c5584830ebc1011849f41b1077c3d6e3c2a6e94e36a338fc6b540c4b736751775e7069df4b257fa3786c1140a2 |
| ssdeep | 96:bFlm4Dt94EugELCBt+qRAVfOTqM8+U00RO:Blz94ExtlRAITqGQO |
| Entropy | 5.690466 |
Set 2
See Table 4 through Table 5 for metadata of the analyzed malware.
| Filename | web-install.jar |
|---|---|
| Size | 8728 bytes |
| Type | JAR |
| MD5 | 32f5c3c1582a77c004b1511c77454678 |
| SHA1 | 2a96ce17ed8a025dd72f3729c247dfdb5b0a19a4 |
| SHA256 | b618057de9a8bba95440f23b9cf6374cc66f2acd127b3d478684b22d8f11e00b |
| SHA512 | ec3880dfdc23a06cc1d97153963c3b0bd64db0469069e8dc3395101d12c65bcdcf87e5eac967ddf0b6be7e1dd6e8faaa233224f9f76a90f44f0e9df320d051a3 |
| ssdeep | 192:omBb/dSBuj9MLFgWfXsea1Xld+LXxzRlRX+pi+n9PshE6w0Tipbg8:j/T9MLFgWfcnVlSzspic9kCPxpB |
| Entropy | 7.923820 |
| Filename | WebAndroidAppInstaller.class |
|---|---|
| Size | 16120 bytes |
| Type | compiled Java class data, version 52.0 (Java 1.8) |
| MD5 | 8387a7ce9f2520d8956747fd247b19af |
| SHA1 | 9808ab3ddfb9ab4fe3af1b5d1f6a638bc03788e0 |
| SHA256 | df501b238854d6579cafebeba82581a728e89ed1f6cd0da54c79ef4eb6f4f9fd |
| SHA512 | a51943a8381e67aca4b8296c9df0b05450525b5b27efbf873fd54a7f68febb503e1eb088d287e3561137fd33d3772dd879a3f00b09285a67f215f7a420e7ffcd |
| ssdeep | 384:iI+1BxqQ3evK5c7aIUnKzaxckO05xiZMQn5JI3c+AK8:iImfqQ3z/nbax1 |
| Entropy | 5.950145 |
Malware Functionality
Set 1
This set of malware contains a loader, a manager, and a malicious listener.
Loader 1
Loader 1 is a Java Archive (JAR) file that contains [T1027.009] and loads the compiled Java class file ReflectUtil.class at runtime.
Loader 1 masquerades ReflectUtil.class as part of the org.apache.http package [T1036]. See Figure 1 for ReflectUtil.class’s hierarchal file path.
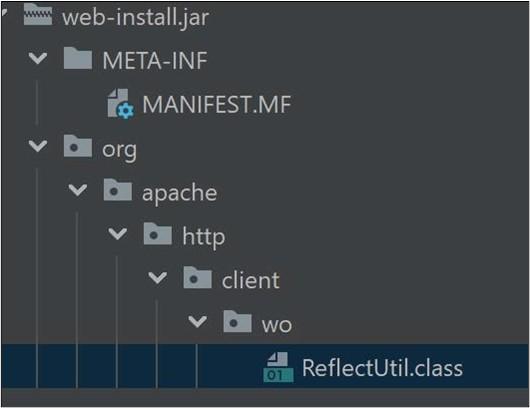
ReflectUtil.class Manager
ReflectUtil.class manipulates Java objects to inject and manage the malicious listener SecurityHandlerWanListener in Apache Tomcat (which was running on the same compromised server). When executed, the file:
- Bypasses Java Development Kit (JDK) module restrictions.
- Iterates objects and their contexts.
- Attempts to load
SecurityHandlerWanListenerclass in the JUnit environment or framework by usinggetClassName()to return the hard-coded stringorg.junit.SecurityHandlerWanListener[T1620].
If SecurityHandlerWanListener class is not loaded because it is not found when ReflectUtil.class first executes, ReflectUtil.class handles the error by using a Base64 string catch block (Figure 2) to Base64 decode, gzip decompress, and load the class SecurityHandlerWanListener.
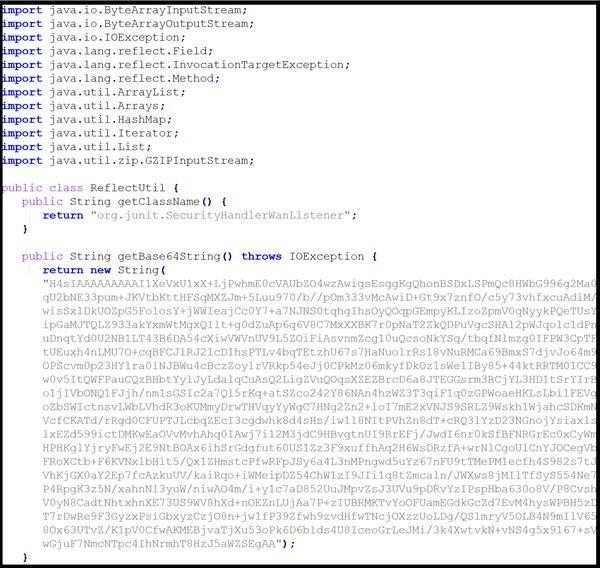
The Base64 string:
- Returns the Base64-encoded and gzip-compressed bytecode of class
SecurityHandlerWanListener. - Decodes and decompresses [T1140] the class bytecode (see Figure 3) in one of two ways:
- It first uses
sun.misc.BASE64Decoderto calldecodeBuffer. - If the first attempt fails, it uses
java.util.Base64to callgetDecoder.
- It first uses
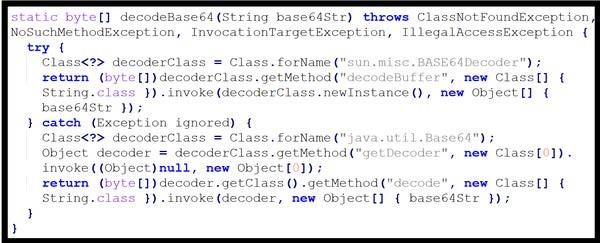
- Invokes the
defineClassmethod ofClassLoaderto load the class from the decompressed bytecode.
Once the class SecurityHandlerWanListener is loaded, ReflectUtil.class:
- Creates a new instance of the class and returns it as a new listener.
- Retrieves the current list of listeners, adds the new listener to this list, and updates the application's listener list.
- Checks if
evilClassNamehas already been injected into the application's event listener list to avoid multiple injections or to confirm a previous injection. (CISA has no additional information on the listenerevilClassName.)
SecurityHandlerWanListener.class
This compiled Java class file is a malicious listener that intercepts specific HTTP requests and processes them to decode and decrypt payloads, which dynamically create and execute a new class.
The file uses ClassLoader to set up a custom servlet listener that intercepts HTTP requests [T1071.001] based on String Pass, Header Name, and Header Values. Specifically, when a new HTTP request is received, the servlet listener checks if the request contains the string pass 7c6a8867d728c3bb, Header Name Referer, and Header Value https://www[.]live.com.
If the fields match, the file creates a HashMap to store the request, response, and session objects. The file also stores the key 7c6a8867d728c3bb in the session.
The file then retrieves, decodes, and decrypts the Base64-encoded payload:
- The file retrieves the payload by reading a line from request’s input stream (
request.getReader().readLine()). - The file decodes the line using Base64.
- The file decrypts the decoded data using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) cipher object with the stored key.
The file passes the decrypted data to a method named g, which defines and creates a new Java class file. Cyber threat actors can execute the class on the device to run arbitrary code.
Potential impact: This listener could allow cyber threat actors to:
- Inject and execute arbitrary code on the server, enabling follow-on activity and persistence.
- Exfiltrate data by intercepting and processing HTTP requests.
See Figure 4 for the relevant listener code snippet.

Set 2
This set of malware contains a loader and a malicious listener.
Loader 2
This JAR file contains and loads the compiled Java class file WebAndroidAppInstaller.class at runtime.
The JAR file masquerades the class file as part of the com.mobileiron.service package. See Figure 5 for WebAndroidAppInstaller.class’s hierarchal file path.
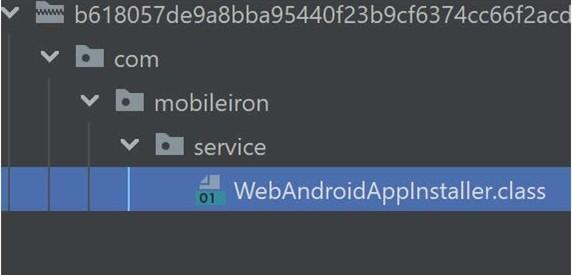
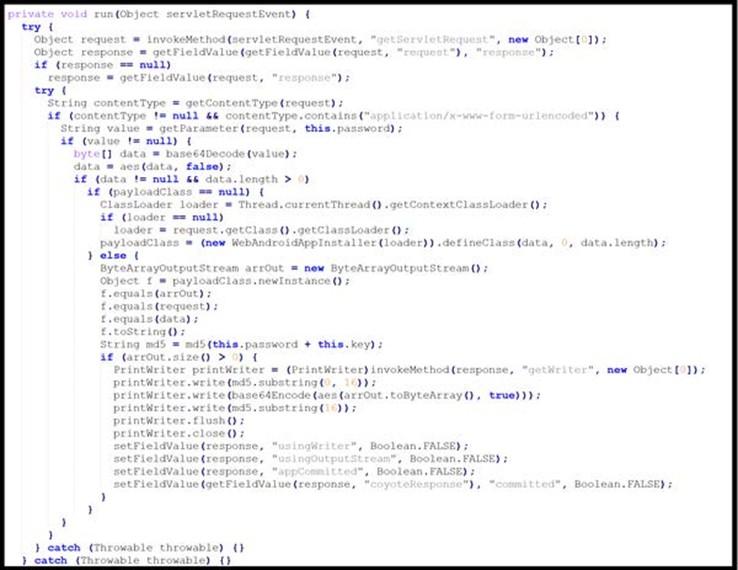
WebAndroidAppInstaller.class
This compiled Java class file is a malicious listener that intercepts and processes specific HTTP requests, retrieves and decrypts password parameters from the request, defines and loads a new malicious class, encrypts and encodes the new class output, and generates a response with the encrypted output.
The listener first retrieves request and response objects from a Java ServletContext. Then, the file checks the request’s Content-Type to ensure it is not null and contains the string application/x-www-form-urlencoded.
If these conditions are met, the file retrieves a password parameter from the request. If the data is not null and has a length greater than zero, the password parameter value is Base64 decoded and decrypted using an AES algorithm with the hard-coded key 3c6e0b8a9c15224a [T1573.001].
If the decrypted data is not empty, the decrypted data defines and implements a new class. The file AES encrypts the new class output using the same hard-coded key, 3c6e0b8a9c15224a, and then Base64 encodes it [T1027.013].
The file then generates a Message Digest Algorithm 5 (MD5) hash of the data stored in the password parameter (from the initial HTTP request) and hard-coded key and checks if the hash value was stored in newly allocated byte array ByteArrayOutputStream. The file creates a PrintWriter object to generate a response containing the first 16 characters of the computed MD5 hash value, followed by the Base64-encoded and AES-encrypted output of the new loaded class and the remaining part of the MD5 hash value.
Potential impact. This listener could allow cyber threat actors to:
- Inject and execute arbitrary code on the server, enabling follow-on activity and persistence.
- Exfiltrate data by receiving response and execution results.
See Figure 6 for the applicable Java code Snippet.
Detection
Yara Rules
Deploy the CISA-created YARA rules in Table 6 to detect malicious activity.
| Loader 1 |
|
rule CISA_251126_01 : trojan hides_artifacts { meta: author = “CISA Code & Media Analysis” incident = “251126” date = “2025-07-23” last_modified = “20250724_1615” actor = “n/a” family = “n/a” capabilities = “hides-artifacts” malware_type = “trojan” tool_type = “unknown” description = “Detects malicious jar filter samples” sha256_1 = “c1f60ca5a5f7b94ab7122718a44b46de16c69d22c2eb62ce2948cab14bc78d50” strings: $s0 = { 6F 72 67 2F 61 70 61 63 68 65 2F 68 74 74 70 2F 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 } $s1 = { 2F 77 6F 2F 52 65 66 6C 65 63 74 55 74 69 6C 2E 63 6C 61 73 73 } $s2 = { 83 2E 9D 42 02 A3 81 42 02 B3 C7 57 34 C4 A8 21 } $s3 = { 8C 8E C0 B6 14 0E 92 08 89 EE EB 1A 11 7D F4 4E } $s4 = { 5B 97 FF F6 12 C9 16 F5 17 C8 5B 5F 44 0E 07 30 } $s5 = { A9 21 59 ED 8E 7A 28 D6 29 FA E3 D0 4C 3D 0F CE } $s6 = { 5A BD F7 24 E8 66 5F 07 2F 7C 0C 0E A9 E3 8D C5 } $s7 = { 05 1B AE 97 B1 88 FF 01 16 EF 3F 44 9E 5F 43 AE } condition: all of them } |
| ReflectUtil.class |
|
rule CISA_251126_02 : trojan { meta: author = “CISA Code & Media Analysis” incident = “251126” date = “2025-07-23” last_modified = “20250724_1615” actor = “n/a” family = “n/a” capabilities = “n/a” malware_type = “trojan” tool_type = “unknown” description = “Detects malicious servlet filter class loader samples” sha256_1 = “065c1c2fb17ba1c3f882bead409215df612673cd455698768ed71412f9190ba3” strings: $s0 = { 6F 72 67 2F 61 70 61 63 68 65 2F 68 74 74 70 } $s1 = { 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 2F 77 6F 2F 52 65 66 6C 65 63 74 55 74 69 6C } $s2 = { 53 65 63 75 72 69 74 79 48 61 6E 64 6C 65 72 57 61 6E 4C 69 73 74 65 6E 65 72 } $s3 = { 67 65 74 4C 69 73 74 65 6E 65 72 } $s4 = { 61 64 64 4C 69 73 74 65 6E 65 72 } $s5 = { 54 6F 6D 63 61 74 45 6D 62 65 64 64 65 64 43 6F 6E 74 65 78 74 } $s6 = { 67 7A 69 70 44 65 63 6F 6D 70 72 65 73 73 } $s7 = { 67 65 74 41 70 70 6C 69 63 61 74 69 6F 6E 45 76 65 6E 74 4C 69 73 74 65 6E 65 72 73 } $s8 = { 73 65 74 41 70 70 6C 69 63 61 74 69 6F 6E 45 76 65 6E 74 4C 69 73 74 65 6E 65 72 73 } $s9 = { 65 76 69 6C 43 6C 61 73 73 4E 61 6D 65 } condition: all of them } |
| SecurityHandlerWanListener.class |
|
rule CISA_251126_03 : trojan installs_other_components exfiltrates_data { meta: author = “CISA Code & Media Analysis” incident = “251126” date = “2025-07-23” last_modified = “20250724_1615” actor = “n/a” family = “n/a” capabilities = “installs-other-components exfiltrates-data” malware_type = “trojan” tool_type = “unknown” description = “Detects malicious servlet filter class samples” sha256_1 = “b1b1cf33b8d3da35293d6b74c378f0cd9452a4351e26d07c896c4d9a8257ef89” strings: $s0 = { 53 65 72 76 6C 65 74 52 65 71 75 65 73 74 4C 69 73 74 65 6E 65 72 } $s1 = { 43 6C 61 73 73 4C 6F 61 64 65 72 } $s2 = { 53 65 72 76 6C 65 74 52 65 71 75 65 73 74 45 76 65 6E 74 } $s3 = { 2F 48 74 74 70 53 65 72 76 6C 65 74 52 65 73 70 6F 6E 73 65 } $s4 = { 48 74 74 70 53 65 73 73 69 6F 6E } $s5 = { 48 74 74 70 53 65 72 76 6C 65 74 52 65 73 70 6F 6E 73 65 } $s6 = { 68 65 61 64 65 72 56 61 6C 75 65 } $s7 = { 37 63 36 61 38 38 36 37 64 37 32 38 63 33 62 62 } $s8 = { 70 61 73 73 } $s9 = { 53 65 63 72 65 74 4B 65 79 53 70 65 63 } $s10 = { 15 68 74 74 70 73 3A 2F 2F 77 77 77 2E 6C 69 76 65 2E 63 6F 6D 2F } $s11 = { 52 65 66 65 72 65 72 } condition: all of them } |
| Loader 2 |
|
rule CISA_251126_04 : trojan hides_artifacts { meta: author = “CISA Code & Media Analysis” incident = “251126” date = “2025-07-23” last_modified = “20250724_1615” actor = “n/a” family = “n/a” capabilities = “hides-artifacts” malware_type = “trojan” tool_type = “unknown” description = “Detects malicious jar Tomcat listener shell samples” sha256_1 = “b618057de9a8bba95440f23b9cf6374cc66f2acd127b3d478684b22d8f11e00b” strings: $s0 = { 63 6F 6D 2F 6D 6F 62 69 6C 65 69 72 6F 6E 2F 73 65 72 76 69 63 65 2F } $s1 = { 57 65 62 41 6E 64 72 6F 69 64 41 70 70 49 6E 73 74 61 6C 6C 65 72 2E 63 6C 61 73 73 } $s2 = { 5A 5D BB 33 C0 43 31 B0 2D DC 58 F2 75 44 CE E5 } $s3 = { 97 DC AC 0F A7 69 97 A4 5A 72 E8 96 AC 43 9E 01 } $s4 = { E0 E0 7E 40 F3 F8 87 30 C5 83 30 C5 43 14 E7 67 } $s5 = { DB E6 F7 F9 BD FC BE 75 00 BF 6F B3 59 B7 28 07 } $s6 = { C6 BF A4 1D 28 AB 7A B9 3E 09 B1 D8 E2 FA 09 36 } $s7 = { B8 0E 8E 0B 97 2D AE CF B4 B8 6E CD E5 E6 BA 92 } condition: all of them } |
| WebAndroidAppInstaller.class |
|
rule CISA_251126_05 : trojan installs_other_components exfiltrates_data { meta: author = “CISA Code & Media Analysis” incident = “251126_” date = “2025-07-23” last_modified = “20250724_1615” actor = “n/a” family = “n/a” capabilities = “installs-other-components exfiltrates-data” malware_type = “trojan” tool_type = “unknown” description = “Detects malicious Tomcat listener shell class samples” sha256_1 = “df501b238854d6579cafebeba82581a728e89ed1f6cd0da54c79ef4eb6f4f9fd” strings: $s0 = { 43 6C 61 73 73 4C 6F 61 64 65 72 } $s1 = { 6D 6F 62 69 6C 65 69 72 6F 6E 2F 73 65 72 76 69 63 65 } $s2 = { 57 65 62 41 6E 64 72 6F 69 64 41 70 70 49 6E 73 74 61 6C 6C 65 72 } $s3 = { 61 64 64 4C 69 73 74 65 6E 65 72 } $s4 = { 73 65 72 76 6C 65 74 52 65 71 75 65 73 74 4C 69 73 74 65 6E 65 72 43 6C 61 73 73 } $s5 = { 61 64 64 41 70 70 6C 69 63 61 74 69 6F 6E 45 76 65 6E 74 4C 69 73 74 65 6E 65 72 4D 65 74 68 6F 64 } $s6 = { 62 61 73 65 36 34 44 65 63 6F 64 65 } $s7 = { 63 6F 6E 74 65 6E 74 54 79 70 65 } $s8 = { 08 72 65 73 70 6F 6E 73 65 } $s9 = { 33 63 36 65 30 62 38 61 39 63 31 35 32 32 34 61 } $s10 = { 6B 70 61 73 73 6C 6F 67 69 6E } $s11 = { 53 65 72 76 6C 65 74 52 65 71 75 65 73 74 4C 69 73 74 65 6E 65 72 } $s12 = { 53 65 63 72 65 74 4B 65 79 53 70 65 63 } condition: all of them } |
SIGMA Rule
Deploy the CISA-created SIGMA rule in Table 7 to detect malicious activity.
| Loader Malware for Ivanti Mobile Management Systems |
|---|
|
## CISA Code & Media Analysis ## ############ README ############### ## Edit rules and queries as needed for your hunt and based on your environment. ## Ensure your EDR/SIEM instance has enough memory to run these AND/OR condition-based queries. May take longer to run than conventional Sigma rule query. ## Do not edit “logsource-product:” unless you are editing this rule to meet specific logsources/fields and know your environment. ## TLP CLEAR may convert rules using online converter of choice. ################################### title: Detects Artifacts Based on MAR-251126, Ivanti EPMM CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428 incident: 251126 tlp: CLEAR id: 83df757f-54e7-44a0-be21-ae2306ca3240 status: test description: Detects abused URL paths and suspicious commands used by Threat Actors on Ivanti Endpoint Manger Mobile (EPMM). Based on MAR-251126 as well as Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428. references: - ‘MAR-251126’ - ‘https://projectdiscovery.io/blog/ivanti-remote-code-execution’ - ‘https://labs.watchtowr.com/expression-payloads-meet-mayhem-cve-2025-4427-and-cve-2025-4428/’ - ‘https://www.wiz.io/blog/ivanti-epmm-rce-vulnerability-chain-cve-2025-4427-cve-2025-4428’ - ‘https://threatprotect.qualys.com/2025/05/20/cisa-warns-of-ivanti-epmm-unauthenticated-remote-code-execution-vulnerabilities-cve-2025-4427-cve-2025-4428/’ - ‘https://profero.io/blog/ivanti-epmm-attacks’ - ‘https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework/blob/26156dfac2e01379eb858a87aa85e2ecfea929ff/modules%2Fexploits%2Fmulti%2Fhttp%2Fivanti_epmm_rce_cve_2025_4427_4428.rb’ author: CISA Code & Media Analysis date: 2025-08-08 modified: 2025-08-13 tags: - cve.2025.4427 - cve.2025.4428 logsource: product: cma detection: keywords: - ‘GET’ keywords_1: - ‘/api/v2/*’ keywords_2: - ‘sh -i’ - ‘invoke’ - ‘java’ - ‘/dev/tcp/’ - ‘getRuntime’ - ‘.jar’ - ‘.class’ - ‘evilClassName’ - ‘ping’ - ‘dig’ - ‘curl’ - ‘wget’ - ‘fetch’ - ‘echo’
keywords_3: - ‘chmod’ keywords_4: - ‘+x’ - ‘a+r’ - ‘755’ - ‘/tmp’
keywords_5: - ‘/mi/tomcat/webapps/mifs/401.jsp’ - ‘/mi/tomcat/webapps/mifs/css/css.css’ - ‘/mi/tomcat/webapps/mifs/session.jsp’ - ‘/mi/tomcat/webapps/mifs/baseURL.jsp’ - ‘065c1c2fb17ba1c3f882bead409215df612673cd455698768ed71412f9190ba3’ - ‘b618057de9a8bba95440f23b9cf6374cc66f2acd127b3d478684b22d8f11e00b’ - ‘c1f60ca5a5f7b94ab7122718a44b46de16c69d22c2eb62ce2948cab14bc78d50’ - ‘df501b238854d6579cafebeba82581a728e89ed1f6cd0da54c79ef4eb6f4f9fd’ - ‘1b1dda5e8e26da568559e0577769697c624df30e’ - ‘ac389c8b7f3d2fcf4fd73891f881b12b8343665b’ - ‘19b4df629f5b15e5ff742c70d2c7dc4dac29a7ce’ - ‘f780151c151b6cec853a278b4e847ef2af3dbc5d’ - ‘dce8faf5fcf5998b6802995914caa988ee1ebd92’ - ‘aa2cfeeca6c8e7743ad1a5996fe5ccc3d52e901d’ - ‘2bd61ce5bdd258c7dcbef53aedb1b018b8e0ae26’ - ‘82.132.235.212’ - ‘37.219.84.22’ - ‘88.194.29.21’ - ‘27.25.148.183’ - ‘83.229.126.234’ - ‘91.193.19.109’ - ‘47.120.74.19’ - ‘100.26.51.59’ - ‘150.241.71.231’ - ‘75.170.92.132’ - ‘5.181.159.149’ - ‘45.38.17.43’ - ‘75.170.92.132’
condition: keywords and keywords_1 and keywords_2 or keywords and keywords_1 and keywords_3 or keywords_3 and keywords_4 or keywords_5
falsepositives: - Rate of FP low-moderate with some strings. - Use this rule in an infected environment/logs. - Analyst may need to make adjustments to the query as required. level: high |
Incident Response
If this or similar malware is detected, CISA recommends that organizations:
- Quarantine or take offline potentially affected hosts.
- Collect and review artifacts, such as running processes/services, unusual authentications, and recent network connections.
- Capture a full forensic disk image of the affected host for sharing with CISA.
- If initial investigation (Step 2) finds the threat actor’s access was limited (e.g., they did not move laterally or elevate privileges), provision new account credentials. If the investigation finds the threat actor had broader access or potentially moved laterally, follow your organization’s incident response plans to initiate threat hunting, containment, and eviction measures.
- Report the compromise to CISA:
- Report the compromise via CISA’s 24/7 Operations Center (contact@cisa.dhs.gov or 1-844-729-2472) or CISA’s Incident Reporting System.
- Use CISA’s Malware Analysis Submission Form to submit a file containing the malicious code. Include the CISA-provided Incident ID number (obtained from reporting the compromise) in the Open Incident ID field.
- Reimage compromised hosts.
- Apply recommendations from the Mitigations section to harden the systems.
Mitigations
CISA recommends organizations implement the mitigations below to improve your organization’s cybersecurity posture on the basis of the threat actors’ activity. These mitigations align with the Cross-Sector Cybersecurity Performance Goals (CPGs) developed by CISA and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The CPGs provide a minimum set of practices and protections that CISA and NIST recommend all organizations implement. CISA and NIST based the CPGs on existing cybersecurity frameworks and guidance to protect against the most common and impactful threats, tactics, techniques, and procedures. Visit CISA’s CPGs webpage for more information on the CPGs, including additional recommended baseline protections.
- Upgrade Ivanti EPMM versions to the latest version as soon as possible.
- Treat mobile device management (MDM) systems as high-value assets (HVAs) with additional restrictions and monitoring. MDM systems provide elevated access to thousands of hosts and should be treated as HVAs with additional restrictions and monitoring.
- Follow best cybersecurity practices in production and enterprise environments, including mandating phishing-resistant multifactor authentication (MFA) for all staff and services. For additional best practices, see CISA’s Cross-Sector Cybersecurity Performance Goals (CPGs).
Disclaimer
CISA does not endorse any commercial entity, product, company, or service, including any entities, products, companies, or services linked within this document. Any reference to specific commercial entities, products, processes, or services by service mark, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise, does not constitute or imply endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by CISA.
Version History
September 18, 2025: Initial version.
Appendix A: MITRE ATT&CK Techniques
See Table 8 and Table 9 for all referenced threat actor tactics and techniques in this advisory. For assistance with mapping malicious cyber activity to the MITRE ATT&CK framework, see CISA and MITRE ATT&CK’s Best Practices for MITRE ATT&CK Mapping and CISA’s Decider Tool.
| Technique Title | ID | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Obfuscated Files or Information: Compile After Delivery | T1027.004 | The cyber threat actors delivered malware in segments, splitting it into multiple Base64-encoded segments. The actors used Java EL injection to write each chunk and append them together using the append mode (via the true parameter). |
| Obfuscated Files or Information: Embedded Payloads | T1027.009 | Loader 1 contains ReflectUtil.class. |
| Obfuscated Files or Information: Encrypted/Encoded File | T1027.013 | WebAndroidAppInstaller.class AES encrypts and Base64 encodes a class output with a hard coded key. |
| Masquerading | T1036 |
Loader 1 masquerades Loader 2 masquerades |
| Reflective Code Loading | T1620 | ReflectUtil.class reflectively loads code into Java processes to add a malicious listener to Apache Tomcat servers. |
| Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information | T1140 | ReflectUtil.class decodes and decompresses a class bytecode. |
| Technique Title | ID | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | T1071.001 |
|
| Encrypted Channel: Symmetric Cryptography | T1573.001 | WebAndroidAppInstaller.class decodes a Base64 password parameter value using an AES algorithm and hard-coded key. |
This product is provided subject to this Notification and this Privacy & Use policy.




